Topic 2, Exam Pool B
Refer to the exhibit.
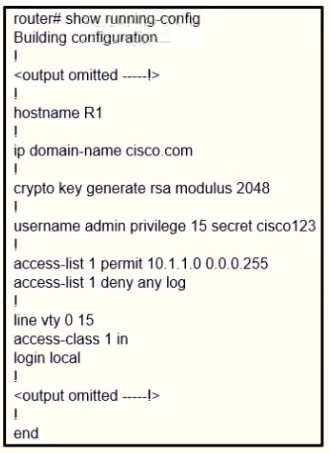
A user cannot SSH to the router. What action must be taken to resolve this issue?
A.
Configure transport input ssh
B.
Configure transport output ssh
C.
Configure ip ssh version 2
D.
Configure ip ssh source-interface loopback0
Configure transport input ssh
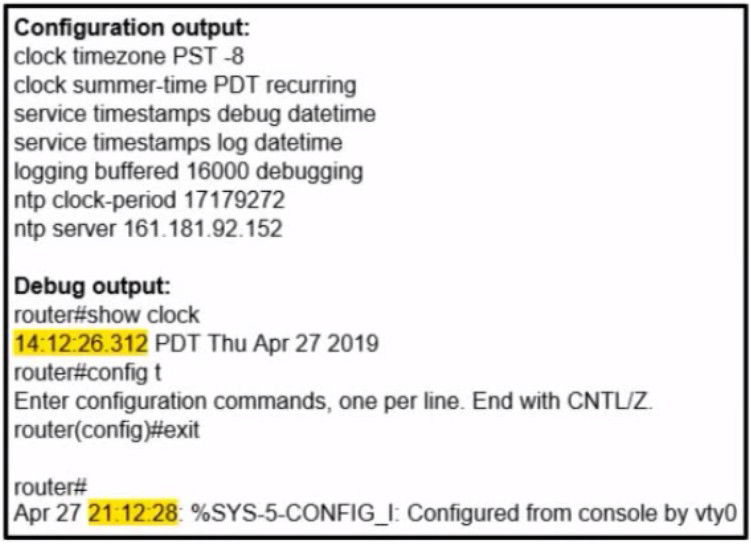
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator configured NTP on a Cisco router to get synchronized time for system and logs from a unified time source The configuration did not work as desired Which service must be enabled to resolve the issue?
A.
Enter the service timestamps log datetime localtime global command.
B.
Enter the service timestamps log datetime synchronize global command.
C.
Enter the service timestamps log datetime console global command.
D.
Enter the service timestamps log datetime clock-period global command
Enter the service timestamps log datetime localtime global command.
Refer to the exhibit.
An IT staff member comes into the office during normal office hours and cannot access devices through SSH Which action should be taken to resolve this issue?
A.
Modify the access list to use the correct IP address.
B.
Configure the correct time range.
C.
Modify the access list to correct the subnet mask
D.
Configure the access list in the outbound direction.
Modify the access list to use the correct IP address.
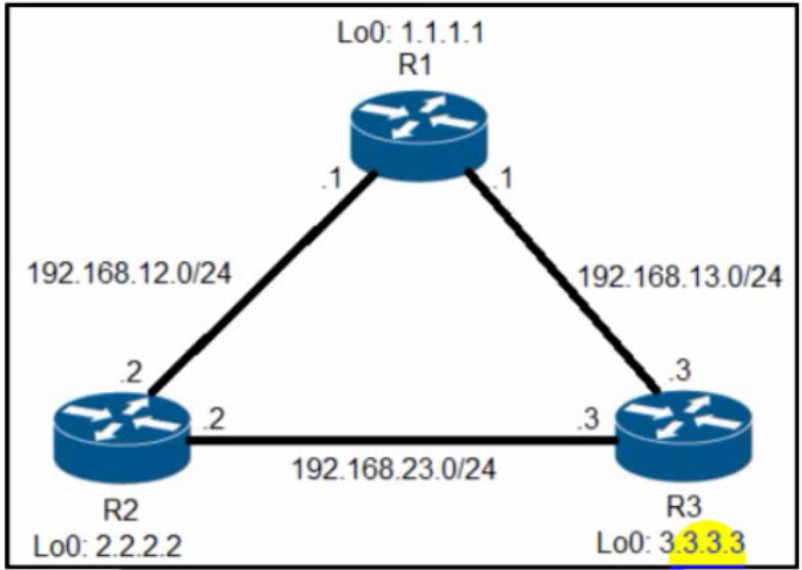

Refer to the exhibit. R2 has two paths to reach 192.168.13.0/24. but traffic is sent only through R3. Which action allows traffic to use both paths?
A.
Configure the bandwidth 2000 command under interface FastEthernet0/0 on R2.
B.
Configure the variance 4 command under the EIGRP process on R2.
C.
Configure the delay 1 command under interface FastEthernet0/0 on R2.
D.
Configure the variance 2 command under the EIGRP process on R2
Configure the variance 4 command under the EIGRP process on R2.
Refer to the exhibit.
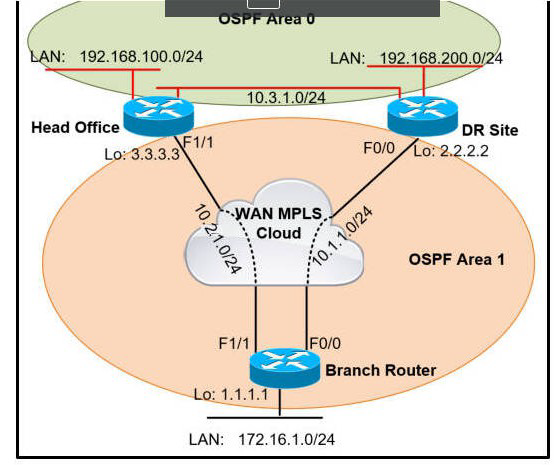
A network administrator reviews the branch router console log to troubleshoot the OSPF adjacency issue with the DR router. Which action resolves this issue?
A.
Advertise the branch WAN interface matching subnet for the DR site.
B.
Configure matching hello and dead intervals between sites.
C.
Configure the WAN interface for DR site in the related OSPF area.
D.
Stabilize the DR site flapping link to establish OSPF adjacency.
Advertise the branch WAN interface matching subnet for the DR site.
A network administrator is tasked to permit http and https traffic only toward the internet from the User1 laptop to adhere to company’s security policy. The administrator can still ping to www.cisco.com Which interface should the access list 101 be applied to resolve this issue?
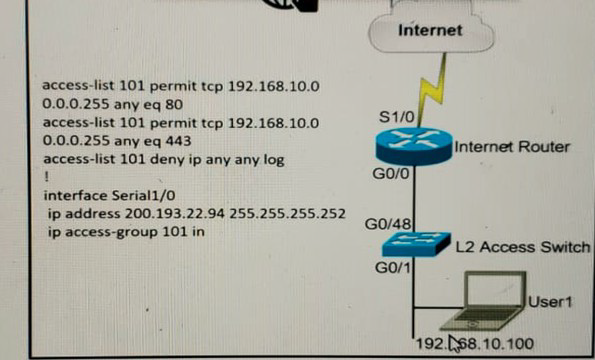
A.
Interface G0/48 in the incoming direction
B.
Interface G0/0 in the outgoing direction.
C.
Interface S1/0 in the outgoing direction.
D.
Interface G0/0 in the incoming direction.
Interface G0/0 in the incoming direction.
An engineer configured Reverse Path Forwarding on an interface and noticed that the routes are dropped when a route lookup fails on that interface for a prefix that is available in the routing table Which interface configuration resolves the issue?
A.
ip verify unicast source reachable-via rx
B.
ip verify unicast source reachable-via any
C.
ip verify unicast source reachable-via allow-default
D.
ip verify unicast source reachable-via 12-src
ip verify unicast source reachable-via any
Refer to the exhibit.

An engineer receives this error message when trying to access another router in-band from the serial interface connected to the console of R1. Which configuration is needed on R1 to resolve this issue?

A.
Option A
B.
Option B
C.
Option C
D.
Option D
Option D
An engineer configured two routers connected to two different service providers using BGP with default attributes. One of the links is presenting high delay, which causes slowness in the network. Which BGP attribute must the engineer configure to avoid using the highdelay ISP link if the second ISP link is up?
A.
LOCAL_PREF
B.
MED
C.
WEIGHT
D.
AS-PATH
LOCAL_PREF
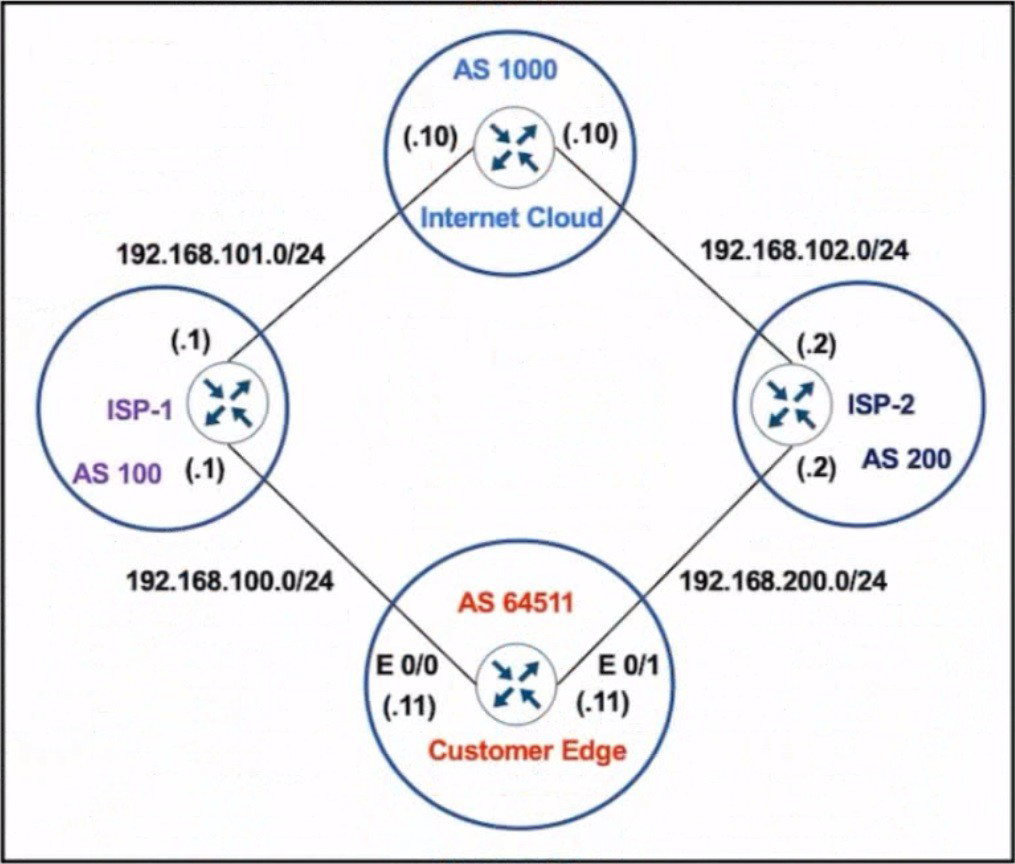
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator has configured the Customer Edge router (AS 64511) to send only summarized routes toward ISP-1 (AS 100) and ISP-2 (AS 200).
router bgp 64511
network 172.16.20.0 mask 255.255.255.0
network 172.16.21.0 mask 255.255.255.0
network 172.16.22.0 mask 255.255.255.0
network 172.16.23.0 mask 255.255.255.0
aggregate-address 172.16.20.0 255.255.252.0
After this configuration. ISP-1 and ISP-2 continue to receive the specific routes and the summary route. Which configuration resolves the issue?
A.
router bgp 64511
aggregate-address 172.16.20.0 255.255.252.0 summary-only
B.
router bgp 64511
neighbor 192.168.100.1 summary-only
neighbor 192.168.200.2 summary-only
C.
interface E 0/0
ip bgp suppress-map BLOCK_SPECIFIC
!
interface E 0/1
ip bgp suppress-map BLOCK_SPECIFIC
!
ip prefix-list PL_BLOCK_SPECIFIC permit 172.16.20.0/22 ge 24
!
route-map BLOCK_SPECIFIC permit 10
match ip address prefix-list PL_BLOCK_SPECIFIC
D.
ip prefix-list PL_BLOCK_SPECIFIC deny 172.16.20.0/22 ge 22
ip prefix-list PL BLOCK SPECIFIC permit 172.16.20.0/22
!
route-map BLOCK_SPECIFIC permit 10
match ip address prefix-list PL_BLOCK_SPECIFIC
!
router bgp 64511
aggregate-address 172.16.20.0 255 255.252.0 suppress-map BLOCKSPECIFIC
router bgp 64511
aggregate-address 172.16.20.0 255.255.252.0 summary-only
Explanation: When the aggregate-address command is used within BGP routing, the aggregated address is advertised, along with the more specific routes. The exception to this rule is through the use of the summary-only command. The “summary-only” keyword suppresses the more specific routes and announces only the summarized route.
| Page 15 out of 57 Pages |
| Previous |