Topic 2, Exam Pool B
Refer to Exhibit.
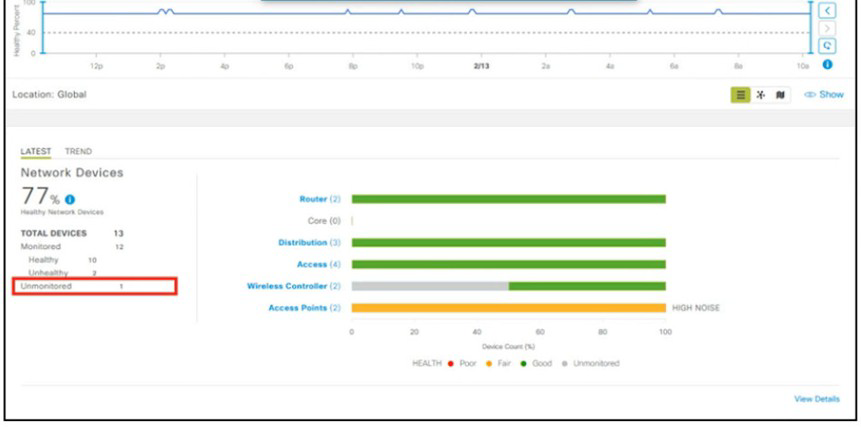
A network administrator added one router in the Cisco DNA Center and checked its discovery and health from the Network Health Dashboard. The network administrator observed that the router is still showing up as unmonitored. What must be configured on the router to mount it in the Cisco DNA Center?
A.
Configure router with NetFlow data
B.
Configure router with the telemetry data
C.
Configure router with routing to reach Cisco DNA Center
D.
Configure router with SNMPv2c or SNMPv3 traps
Configure router with the telemetry data
STION NO: 186
Refer to the exhibit.
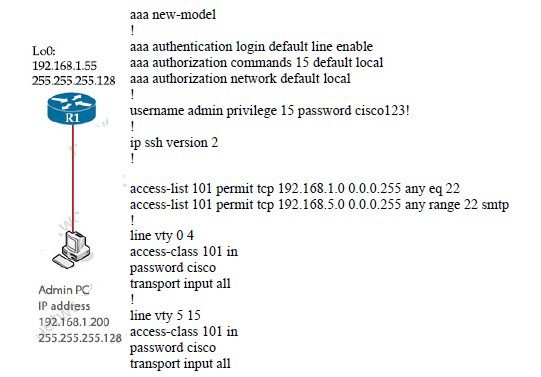
The administrator successfully logs into R1 but cannot access privileged mode commands. What should be configured to resolve the issue?
A.
aaa authorization reverse-access
B.
secret cisco123! at the end of the username command instead of password cisco123!
C.
matching password on vty lines as cisco123!
D.
enable secret or enable password commands to enter into privileged mode
enable secret or enable password commands to enter into privileged mode
Refer to the exhibit.

The neighbor is not coming up. Which two sets of configurations bring the neighbors up? (Choose two.)
A.
R2
ip route 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 192.168.1.1
router bgp 200
neighbor 10.1.1.1 tti-security hops 1
neighbor 10.1.1.1 update-source loopback 0
B.
R2
ip route 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 192.168.1.1
router bgp 200
neighbor 10.1.1.1 disable-connected-check
neighbor 10.1.1.1 update-source loopback 0
C.
R2
ip route 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.255 192.168.1.2
router bgp 100neighbor 10.1.1.2 ttl-security hops 1
neighbor 10.1.1.2 update-source loopback 0
D.
ip route 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.255 192.168.1.2
router bgp 100
neighbor 10.1.1.1 ttl-security hops 1
neighbor 10.1.1.2 update-source loopback 0
E.
ip route 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.255 192.168.1.2
router bgp 100
neighbor 10.1.1.2 disable-connected-check
neighbor 10.1.1.2 update-source Loopback0
R2
ip route 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 192.168.1.1
router bgp 200
neighbor 10.1.1.1 disable-connected-check
neighbor 10.1.1.1 update-source loopback 0
ip route 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.255 192.168.1.2
router bgp 100
neighbor 10.1.1.2 disable-connected-check
neighbor 10.1.1.2 update-source Loopback0
Refer to the exhibit.
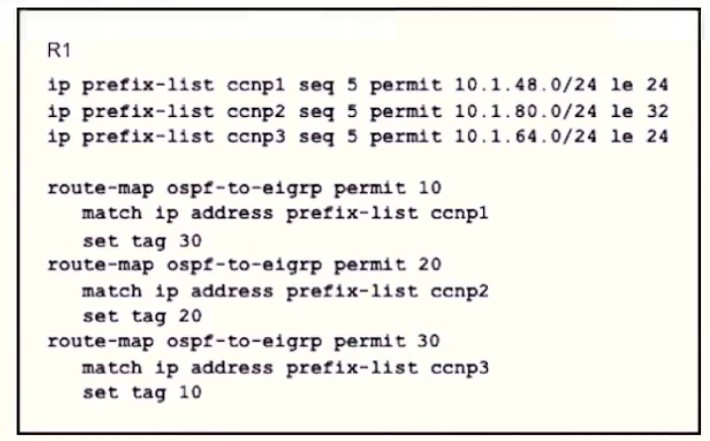
An engineer wanted to set a tag of 30 to route 10 1.80.65/32 but it failed How is the issue fixed?
A.
Modify route-map ospf-to-eigrp permit 30 and match prefix-list ccnp2.
B.
Modify route-map ospf-to-eigrp permit 10 and match prefix-list ccnp2.
C.
Modify prefix-list ccnp3 to add 10.1.64.0/20 le 24
D.
Modify prefix-list ccnp3 to add 10.1.64.0/20 ge 32
Modify route-map ospf-to-eigrp permit 10 and match prefix-list ccnp2.
Refer to the exhibit.
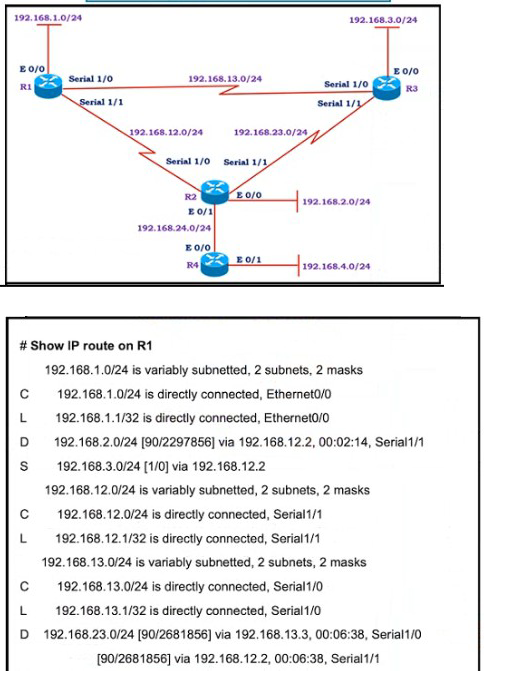
All the serial between R1, R2, and R3 have the Same bandwidth. User on the 192.168.1.0/24 network report slow response times while they access resource on network 192.168.3.0/24. When a traceroute is run on the path. It shows that the packet is getting forwarded via R2 to R3 although the link between R1 and R3 is still up. What must the network administrator to fix the slowness?
A.
Change the Administrative Distance of EIGRP to 5.
B.
Add a static route on R1 using the next hop of R3.
C.
Remove the static route on R1.
D.
Redistribute theR1 route to EIGRP
Remove the static route on R1.
Refer to Exhibit.
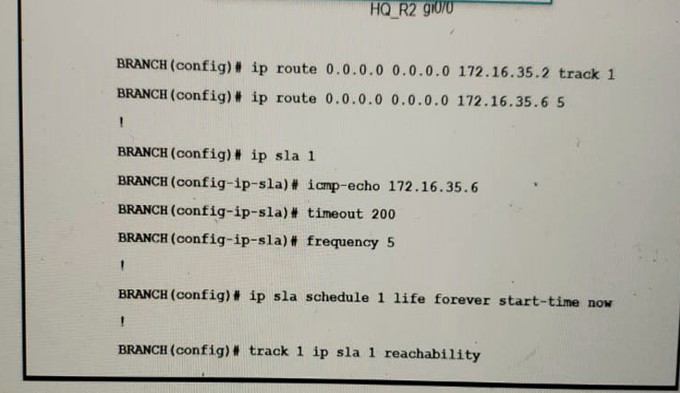
Traffic from the branch network should route through HQ R1 unless the path is unavailable. An engineer tests this functionality by shutting down interface on the BRANCH router toward HQ_R1 router but 192.168.20.0/24 is no longer reachable from the branch router. Which set of configurations resolves the issue?
A.
HQ_R1(config)# ip sla responder
HQ_R1(config)# ip sla responder icmp-echo 172.16.35.2
B.
BRANCH(config)# ip sla 1
BRANCH(config-ip-sla)# icmp-echo 172.16.3
C.
HQ_R2(config)# ip sla responder
HQ_R2(config)# ip sla responder icmp-echo 172.16.35.5
D.
BRANCH(config)# ip sla 1
BRANCH(config-ip-sla)# icmp-echo 172.16.35.2
BRANCH(config)# ip sla 1
BRANCH(config-ip-sla)# icmp-echo 172.16.35.2
Refer to the exhibit.
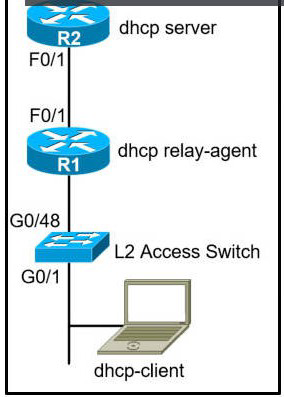
The network administrator can see the DHCP discovery packet in R1. but R2 is not replying to the DHCP request. The R1 related interface is configured with the DHCP helper address. If the PC is directly connected to the FaO/1 interface on R2, the DHCP server assigns as IP address from the DHCP pool to the PC. Which two commands resolve this issue? (Choose two.)
A.
service dhcp-relay command on R1
B.
ip dhcp option 82 command on R2
C.
service dhcp command on R1
D.
ip dhcp relay information enable command on R1
E.
ip dhcp relay information trust-all command on R2
service dhcp command on R1
ip dhcp relay information trust-all command on R2
Refer to the exhibit.
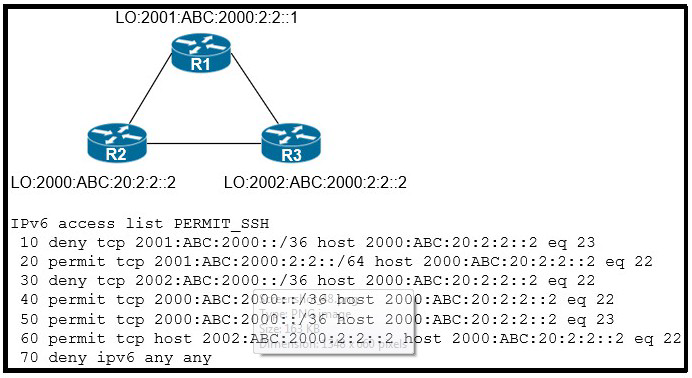
An IPv6 network was newly deployed in the environment and the help desk reports that R3 cannot SSH to the R2s Loopback interface. Which action resolves the issue?
A.
Modify line 10 of the access list to permit instead of deny.
B.
Remove line 60 from the access list.
C.
Modify line 30 of the access list to permit instead of deny.
D.
Remove line 70 from the access list.
Modify line 30 of the access list to permit instead of deny.
Refer to the exhibit.
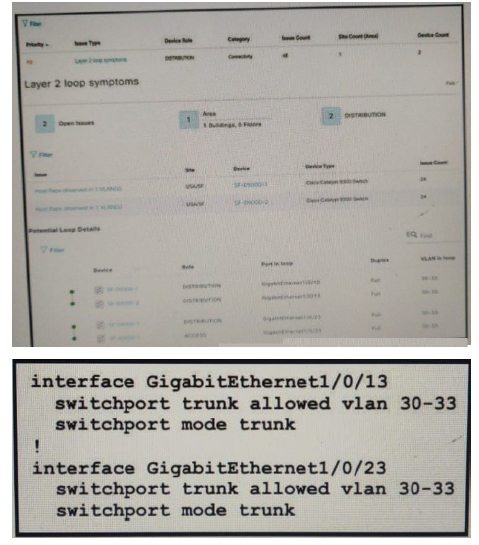
An engineer identifier a Layer 2 loop using DNAC. Which command fixes the problem in the SF-D9300-1 switch?
A.
no spanning-tree uplinkfast
B.
spanning-tree loopguard default
C.
spanning-tree backbonesfast
D.
spanning-tree portfast bpduguard
spanning-tree portfast bpduguard
Refer to the exhibit.
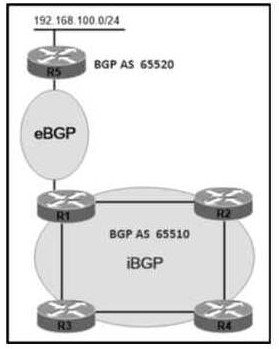
AS65510 iBGP is configured for directly connected neighbors. R4 cannot ping or traceroute network 192 168.100.0/24 Which action resolves this issue?
A.
Configure R4 as a route reflector server and configure R1 as a route reflector client
B.
Configure R1 as a route reflector server and configure R2 and R3 as route reflector clients
C.
Configure R4 as a route reflector server and configure R2 and R3 as route reflector clients.
D.
Configure R1 as a route reflector server and configure R4 as a route reflector client
Configure R1 as a route reflector server and configure R4 as a route reflector client
| Page 21 out of 57 Pages |
| Previous |